Home > Process Modeling and Simulation Concepts > Functions > Mapping Function
The value of the argument passed to a mapping function dictates what value is returned by the function. For example, you could define a mapping function called GetPrice which returns the price of a part based on a part number.
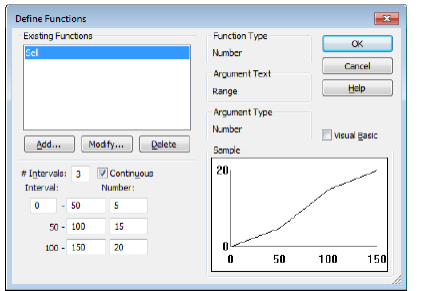
The values returned by a mapping function depend on its input argument. For example, the following figure illustrates a mapping function whose argument value is a number.
|
|
This mapping function has three defined intervals. The intervals specify that if the input number is between 0 and 50, the function returns a value between 0 and 5. If the input number is between 50 and 100, the function returns a value between 5 and 15. If the input number is between 100 and 150, the function returns a value between 15 and 20. Note that while this function returns continuous values, you can define a mapping function to be noncontinuous.
By contrast, the following figure shows a mapping function in which the input arguments are members of the type YesNo.
|
|
If the input argument is Yes, the function returns 1. If the input argument is No, the function returns 0.
Related Topics
See Also